knowledge of results feedback|knowledge of results vs performance : Cebu Knowledge of results focuses on how successfully a skill has been performed and is usually associated with the outcome, such as the distance a javelin has been . Tingnan ang higit pa 10:00 AM Local Time to Eastern Daylight Time. 10:00 AM (10:00) . Daylight Saving Time used for Eastern Standard Time (EST), for details check here. Scale: • Is local time not Right? Input the time zone below to convert: » EDT to Worldwide Timezone Converters • Eastern Daylight Time Offset: UTC -4 .IELTS for UK Visas and Immigration . Learn more about registering for IELTS with the British Council. Chat with us online for your IELTS queries! We are available from 09.00-16.00 (Philippine time), Monday to Saturday. Connections Through Culture grantees announcement 2023
PH0 · knowledge of results vs performance
PH1 · knowledge of results feedback examples
PH2 · knowledge of performance refers to
PH3 · knowledge of performance feedback
PH4 · Iba pa
May Bagong Toy Na Magiging Boytoy ni Majoy . 08:56 HD. Gustong Magsupport ni Brownie
knowledge of results feedback*******Knowledge of Results vs Knowledge of Performance. by Will Shaw PhD, MSc. Feedback is critical when learning any skill. Here we’ll look at two types of feedback – knowledge of results and knowledge of performance. We’ll define both and explain how they can be applied to a sporting context. Tingnan ang higit paThis next section digs into the most commonly asked questions around knowledge of results and how it relates to feedback . Tingnan ang higit pa
knowledge of results feedbackKnowledge of results focuses on how successfully a skill has been performed and is usually associated with the outcome, such as the distance a javelin has been . Tingnan ang higit pa
Knowledge of results allows an athlete to measure how successful they were. Without any knowledge of results learning is . Tingnan ang higit paAn example of knowledge of results is a javelin throwing knowing their attempt landed at 83m. Another example would be a sprinter knowing their 100m time was 11.2 . Tingnan ang higit pa There are two types of augmented feedback and they are known as knowledge of performance and knowledge of results 15, 16, 17). Knowledge of results . Immediate Knowledge of Results (KR) feedback at the task level may motivate test takers by showing that their answers matter. Appealing feedback cues may . Augmented feedback is a key component of motor skill learning. Feedback can provide information relating to the movement outcome (knowledge of results; KR) .knowledge of results feedback knowledge of results vs performance Furthermore, all augmented feedback can be divided into two categories: knowledge of results (KR; information about the outcome of the attempt) and .Knowledge of results and motor learning: a review and critical reappraisal. A number of new relations emerge between KR and both learning and performance, and it is .Knowledge of results is a term in the psychology of learning. [1] [2] : 619 A psychology dictionary defines it as feedback of information: " (a) to a subject about the correctness .
Introduction: Knowledge of results (KR) is a method of augmented feedback where frequency or timing varies depending on the individual’s performance. In previous .
Feedback plays a crucial role in the acquisition of these skills, but little research has explored the effectiveness of augmented (knowledge of results (KR) and knowledge of .
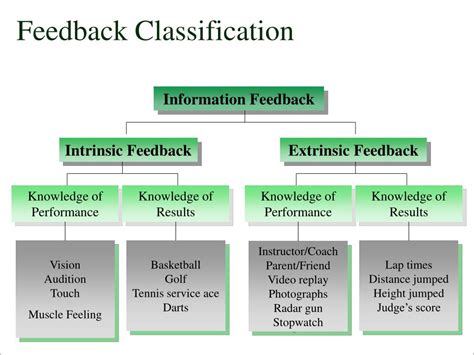
Widely used feedback types are knowledge of performance (provides learners with a summative feedback after they have responded to a set of tasks, i.e., percentage of . From verbal feedback, an arrow leads to the next square holding further specifications of verbal feedback. These are: the focus of the feedback (that is, knowledge of performance versus knowledge of results feedback), and the level of specificity of the feedback (that is, quantitative versus qualitative feedback).Knowledge of performance refers to feedback provided by the SLP that gives the child specific information on how a movement is performed or correction to the specific movement (i.e., ‘your tongue needs to be up more”, “build up that air inside with your lips closed tight”). Knowledge of results refers to feedback from the SLP regarding .
Examines some critical definitional and experimental-design problems that underlie the principles of knowledge of results (KR) and learning, the KR literature, and how newer principles of KR lead to notions of how KR works in human motor-learning situations. KR is defined as augmented feedback, where the KR is additional to those sources of .«knowledge of results» (KR) or «informative feedback», pointing out that sometimes the expression «feedback» is also used. This attitude is quite elucidative of the use of the different designations refering to the same concept - the KR (Table 1). «Knowledge of results» is the most common expression. Schmidt (1988) defines the concept as:Knowledge of results refers to how successfully a skill is performed. It is always external feedback and may come from sources such as a coach, spectators or teammates. Examples of knowledge of results may be how many goals were scored per number of attempts, or what distance was covered in javelin. The athlete can use this feedback to .The quality of the information given to the subject after performance, particulary the Knowledge of Results (KR) precision, seems to have a positive influence on the learning process. In this article, we review the investigation produced in KR precision and emphasize the influence of some variables, like the task characteristics, the development level of .the delay of knowledge of results (KR). Compared with delayed feedback, instantaneous KR should be detrimental to the learning of error-detection capabilities because it should tend to The intrinsic feedback is directly perceptible by the learner as a result of an action. The extrinsic effect comes from information returned to learners by artificial means. One example of an extrinsic feedback is “knowledge of results (KR),” which is information about the success of action to the goal, provided by a third party through . Introduction. Augmented feedback (FB) refers to information that enhances motor learning (Sigrist et al., 2013 ). Augmented FB implies externally informed FB (quantitatively and/or qualitatively) as opposed to intrinsic FB (Lauber & Keller, 2014 ). Knowledge of results (KR) is a type of augmented FB, featuring verbalizable . Abstract Feedback has been shown to influence the extent and rate of learning. The purpose of this research was to investigate the effects of Knowledge of Results (KR) on more accurate trials versus KR on less accurate trials on intrinsic motivation, self-confidence and anxiety changes. Participants were 60 female students . Augmented feedback is defined as feedback from an external source and can be provided as knowledge of result (KR) or knowledge of performance (KP). Whereas the former provides information about the movement outcome (feedback about goal achievements), the latter informs about the quality of the movement execution. The prediction that feedback after every trial would result in more effective skill learning than feedback on only a portion of practice trials is contrary to the generally accepted view regarding the function of augmented feedback for learning, . Knowledge of results and motor learning: a review and critical appraisal. Psychol. Bull. 95, .knowledge of results vs performance( KR : Knowledge of Results) 今回はKRについてです。 これは技能学習の際に行う、フィードバックのことです。 KR にはいくつか種類があり、どの タイミング でフィードバックを行うのか、また、どのような 課題 . Three experiments that explored the role of knowledge of results in motor learning and their impact on motor performance and learning revealed a number of parallel effects, thus providing support for the guidance hypothesis. Recent work on the role of knowledge of results (KR) in motor learning has challenged some traditional . Augmented feedback is a key component of motor skill learning. Feedback can provide information relating to the movement outcome (knowledge of results; KR) or information relating to a movement .Beim extrinsischen Feedback sind grundsätzlich zwei Arten zu unterscheiden: Ergebnisbezogene Rückmeldungen (auch Knowledge of Results oder KR) Verlaufsbezogene Rückmeldungen (auch Knowledge of Performance oder KP) Das Feedback kann sowohl mündlich als auch mit Hilfe von anderen Medien (z. B. .
Augmented feedback can be further classified into two primary dimensions: knowledge of results (KR) and knowledge of performance (KP). KR informs learners about the outcome or consequences of their performance, while KP provides information about the technique, form, or execution of the movement itself [4-5]. To exemplify these feedback types .

Group 1 received knowledge of result as feedback whereas group 2 received knowledge of performance as feedback. In order to enhance motor learning, feedback can be used in any form, especially in .
Macau (traditional Chinese: 澳門 simplified Chinese: 澳门) is a Special Administrative Region (SAR) of the People's Republic of China. Located across the Pearl River estuary from Hong Kong, Macau was until 1999 an overseas territory of Portugal. One of the world's most densely populated spots, Macau generates more revenue from .
knowledge of results feedback|knowledge of results vs performance